Plywood is a popular building material for walls, floors, and ceilings. It’s a good choice if you’re looking for something budget-friendly, lightweight, and durable.
But while Plywood has its limitations, there are other materials you can use to replace it. What if you could use substitute items that are just as strong but much cheaper?
If you’re looking for a possible plywood alternative, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we will review 15 choices. Their advantages and disadvantages, and give you specific recommendations.
When choosing alternatives to Plywood, know that you have 15 options when switching. You can come across materials like Polyurethane Model Board, MDF Board (Medium Density Fiberboard), and Oriented Strand Board (OSB). At the same time, you can use High-Density Fiberboard (HDF), Fiber Cement Board. Meanwhile, Solid Wood and Baltic Birch Plywood are great options too.
Let’s take a look at these alternatives — you might surprise yourself!
15 Great Plywood Alternatives For Walls And Flooring
Instead of using Plywood, let’s consider over a dozen different options.
First, here is a rundown of substitute flooring materials that you can use in place of Plywood. Picking one of them that best fits your needs is the best course of action. In addition, any potential preparation or upkeep may be necessary.
1. Polyurethane Model Board
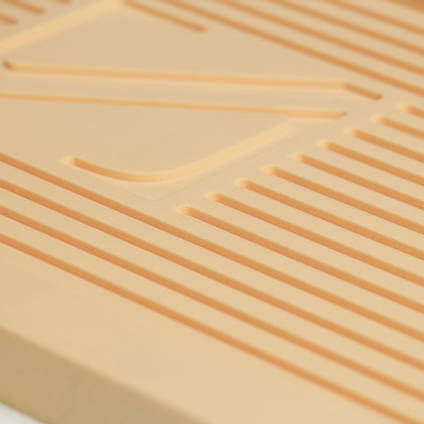

The hardness of the polyurethane model board makes it ideal for manufacturing patterns.
Homeowners can also use it for models and molds for low-volume production runs. In most cases, the density makes hand carving difficult. However, manual or CNC machine tools can produce precise results.
Texture: Compared to plywood, this one is sturdy and has a smoother texture.
Thickness: You can count on them to last longer than plywood boards of the same thickness.
Durability: These foam boards can last long. These materials are impervious to water and highly sturdy.
Density: When compared to a sheet of plywood of the same size, the foam boards are 30–60% lighter.
2. MDF Board (Medium Density Fiberboard)
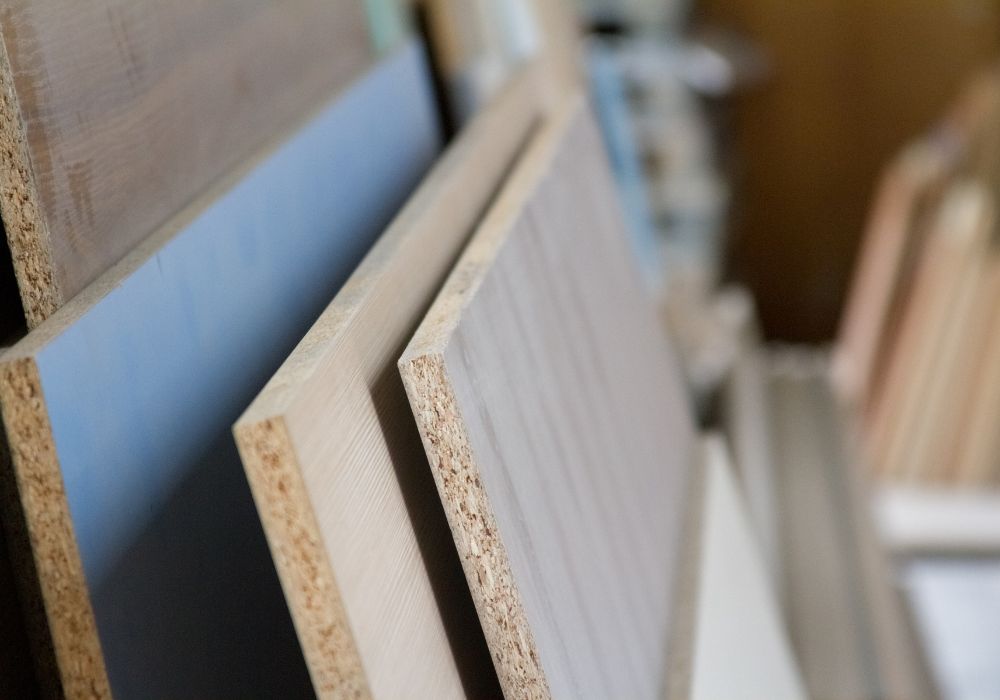

MDF, or medium-density fiberboard, is a composite wood product made from wood fibers. These materials are typically extracted from softwood.
MDF, in contrast to most plywood, has no spaces. Therefore it provides clean cuts without tearout.
Applications: MDF is commonly used for making furniture. These include kitchen cabinets, moldings, millwork, and door parts. Plywood has several uses, including construction materials, roofs, walls, and subfloors.
Structure: MDF’s structure is consistent, smooth, and free of knots. Plywood, on the other hand, has an uneven number of layers. The grains of its layers cross one other at right angles.
Constituents: Wood fibers with wax and resin are substances to create MDF. On the other hand, Plywood is from glued-together thin sheets of veneer.
3. Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
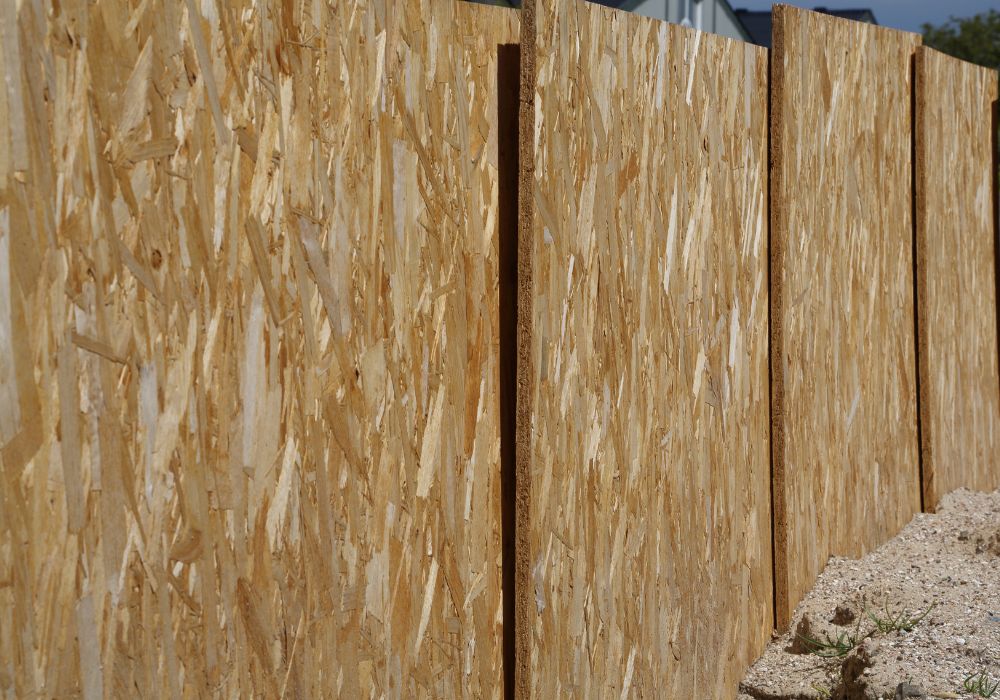

Oriented Strand Board, or OSB, is a flexible engineered wood panel. Manufacturers make it using heat-cured adhesives that are both watertight and non-toxic.
It is a sturdy and stable panel that will not warp under normal conditions. Additionally, it can withstand earthquake and wind forces.
Strength: OSB performs similarly to plywood. This means it is resistant to deflection, warping, and distortion.
Quality: There are no core voids in OSB, and it does not delaminate. It provides more consistent quality than plywood. When exposed to moisture, plywood also delaminates at a higher rate than OSB.
Density: OSB is heavier than plywood. The heavier weight of OSB makes it more challenging to install and adds stress to the building.
4. Reinforced Polyurethane Boards (RPF)
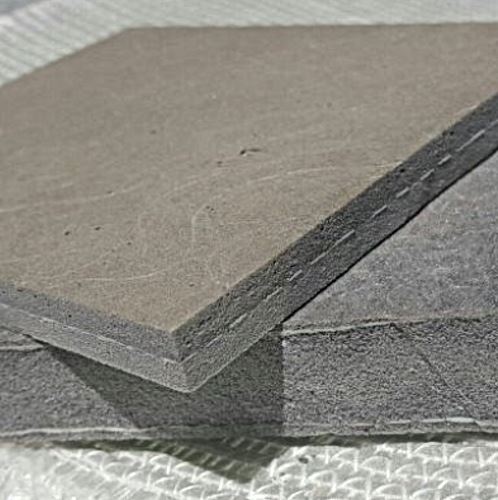

Several businesses use Reinforced Polyurethane Foam (RPF) Boards for structural and semi-structural purposes.
The high-density boards are stronger by layers of fiberglass. As a result, their natural durability prevents them from deteriorating over time. Additionally, RPF has higher adhesion than wood due to its low moisture content.
Density: Composites are 30–45% lower in weight than plywood.
Water Resistance: Have a high strength-to-weight ratio compared with plywood. It absorbs less than 1% of its weight in water.
Strength: In large-scale applications, they may need additional support. RPF is less sturdy than plywood. They may not be ideal for situations where aesthetics is essential.
Cost: Because of their low price, homeowners can use them in various applications. When compared to plywood, the price tag is far more manageable.
5. Particle Board

Particle board, or chipboard, is a type of low-density fiberboard. It’s an artificial wood product made from wood scraps and plastic.
Unlike plywood, it won’t warp or bow but will swell and become unstable if exposed to water.
Holding Capacity: Particle boards aren’t the best choice for nailing heavy objects. This is due to their low holding power and brittleness. Meanwhile, the plywood’s robust composition makes it ideal for nails and screws.
Finish: Upon staining and lacquering; particle boards make a sleek and level appearance. In contrast, rough fibers in plywood necessitate sanding before achieving the finishing touches.
Cost: Particle board is cheaper than plywood. It is frequently produced from wood offcuts. This is why homeowners can purchase it at a lower price.
6. EKO Plyboard Recycled Plastic Sheets
It’s easy to see several potential uses for EKOply plastic sheets. First, they are an excellent replacement for plywood. Second, they consist of 100% recycled plastic.
Manufacturers design each panel to be as functional as imported plywood. In most cases, homeowners can reuse it at end-of-life.
Eco-Friendly: You can entirely recycle EKOply without harming the environment. This means you will never throw away these plastic sheets, unlike plywood.
Cost: Price is not an issue with Ecoply. You may expect their material costs to be lower due to recyclable properties. So, it saves money compared to plywood.
Water Resistance: EKOply is waterproof. It is also long-lasting and doesn’t need much upkeep. Since it is resistant to rot and the elements, it can last much longer than plywood.
7. High-Density Fiberboard (HDF)

High-density fiberboard, or hardboard, is a versatile, inexpensive, and long-lasting building material.
You can use it as an alternative to wood for numerous home improvement projects. Some of these projects are crown molding, flooring, and cabinetry.
Density: Hardness links with density. Densities of HDF typically range from up to 900kg/m3. Thus a denser material will naturally be more durable. In contrast, plywood has a thickness of between 500 and 650 kg/m3. This makes HDF effectively stronger.
Durability: HDF consists of thin wood fiber panels, resin, and wax. If you’re looking for engineered wood, HDF is typically seen as a step above the plywood. It’s more compact, robust, and long-lasting.
Cost: HDF fiberboard is more expensive than MDF. Yet significantly cheaper than plywood material.
8. Fiber Cement Board

Fiber cement boards are composite materials that combine sand, cement, and cellulose fibers.
To be more precise, their core material is cement and glass-fiber mesh. These boards are equally useful when used alone or in combination with plywood.
Applications: You can use cement board for tiled surfaces. These include worktops, bathtubs, and showers. As mentioned earlier, homeowners use plywood for flooring, roofing, and formwork.
Moisture Resistance: Cement boards hold up better in humid and wet conditions. Unlike plywood, it won’t expand and warp over time.
Installation: It’s more expensive to install fiber cement board siding than plywood. More workers are necessary to transport and install fiber cement. Hence labor costs are higher.
9. Solid Wood

To put it simply, solid wood is freshly cut wood from a tree.
The planks used to create solid wood furniture are from old trees. These slabs have reached their full growth and maturity. Examples are maple, oak, redwood, mahogany, ash, beech, teak, rosewood, and cherry.
Properties: Plywood consists of pressing and gluing together thin layers of wood veneer. However, you can get solid wood by sawing trees down.
Weather Resistance: Solid wood will contract and expand due to humidity and temperature. Whereas plywood will not.
Finishing: In contrast to plywood, finishing with paint is far heavier and time-consuming.
Assembly: When compared to solid wood, plywood is both simpler to cut and faster to construct.
10. Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)

Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) is also a fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP). The material is robust, remarkably lightweight, and exceedingly flexible.
With GRP, industrial buildings gain extra durability, stability, and resistance. In addition, GRP profiles are versatile in terms of form and function. This makes them ideal for use in commercial and industrial settings.
Weather Resistance: Compared to plywood, GRP’s weather resilience is impressive. They have a high degree of flexibility and resistance to corrosion.
Quality: You can achieve good quality at a low cost by using GRP over plywood. This is why the construction industry regards it well.
Finishing: Regarding the final touch, you have more color options than with plywood. In addition, using pigments allows for the creation of infinite tonal variations.
11. Baltic Birch Plywood
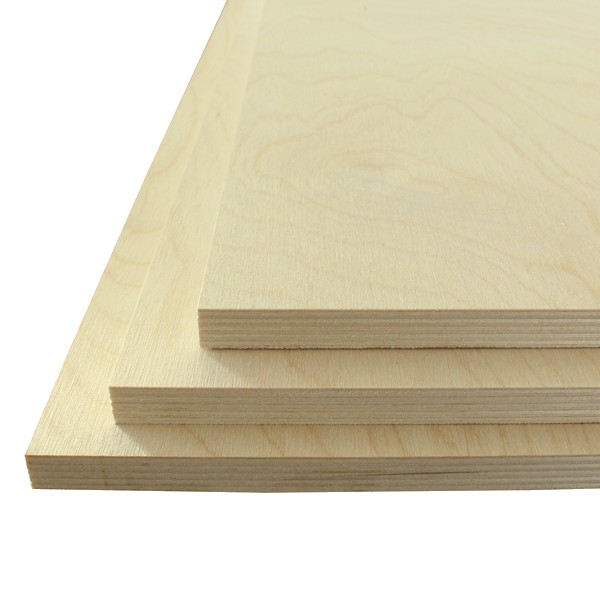

Baltic birch plywood is widely used for cabinet and furniture construction.
Depending on the quality, it’s tougher and more durable than other types of plywood. In addition, it is a more aesthetically pleasing, flat surface.
Distinction: Baltic birch plywood is unique from any other plywood. You may distinguish them due to their all-birch veneer core. This makes them an exceptionally stable sheet.
Layering: In contrast to standard plywood, Birch plywood has several lamination layers. It has nearly no openings or spaces between them.
Strength: Birch plywood can support a greater load with less tension than other woods. This is because of its compact and laminated construction. As a result, birch is stronger than plywood and can withstand shattering.
12. King Starboard HDPE
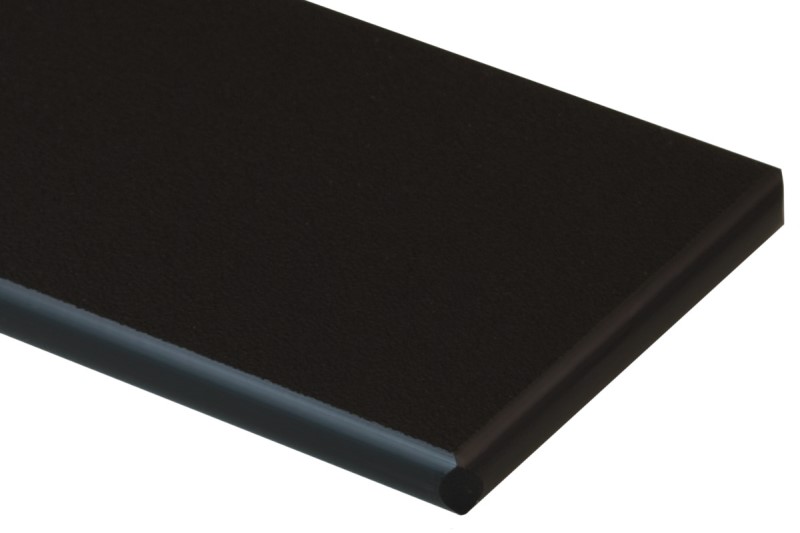

You can think of King StarBoard as a high-density polyethylene plastic (HDPE) variant.
StarBoard sheets are always perfectly flat because of their unique production technique. As a result, HDPE has superior strength and durability over other polymers, wood, and metal.
Durability: King StarBoard has been chemically treated to withstand extreme weather and seawater. It shares neither the weaknesses of teak nor plywood in terms of decay and discoloration. Unlike plywood, they will not split apart.
Installation: You can install King StarBoardan using common woodworking tools. This makes it simple to make adjustments to the design as needed. Moreover, King StarBoard is less expensive to install than plywood.
Weight: King StarBoard features a closed-cell structure to reduce weight. It is a viable alternative because it is around 35% lighter than plywood.
13. Masonite

Masonite is a type of hardboard created from pressed wood fibers. The construction industry uses it as building material and insulation.
Masonite is great for table tennis tables and skateboard ramps due to its flat surface.
Durability: Plywood is long-lasting, although it is not as tough as Masonite. Therefore, you shouldn’t use plywood to carry a lot of weight.
Aesthetics: Masonite is susceptible to stains. You’ll need to use a specialist paint to modify the color. Meanwhile, plywood can take stain and paint quite fine.
Varieties: Masonite purchases come with fewer options. There is little variety in terms of thicknesses. With plywood, your options are extensive. It has a wide variety of colors too.
14. Laminate
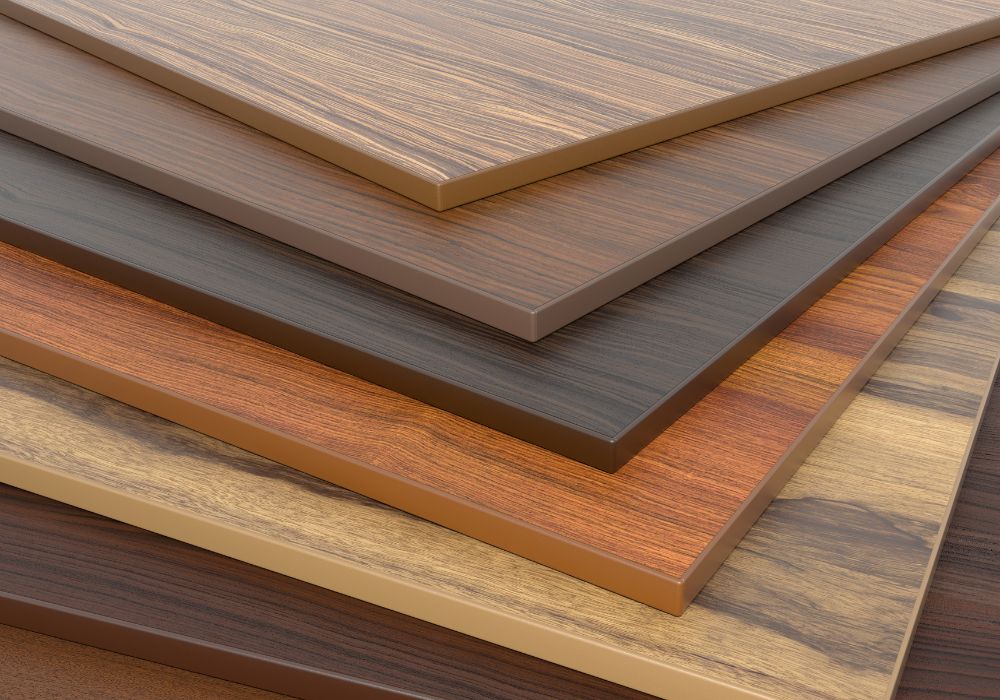

Laminates are one of the most popular choices in the market today.
In addition to its durability and versatility, laminate flooring is low maintenance. It doesn’t last as long as hardwood, but you can get it for half the price, and it’s much easier to install.
Assembly: Lamination is a time-consuming process. It can take a long time to complete a project. In contrast, basic and complex curves can be quickly produced from plywood.
Durability: Laminates, unlike plywood, are scratch-resistant, long-lasting, and simple to maintain. The clear protective layer is resistant to most contaminants.
Structure: Laminates are often smaller than plywood due to their construction.
15. AdvanTech
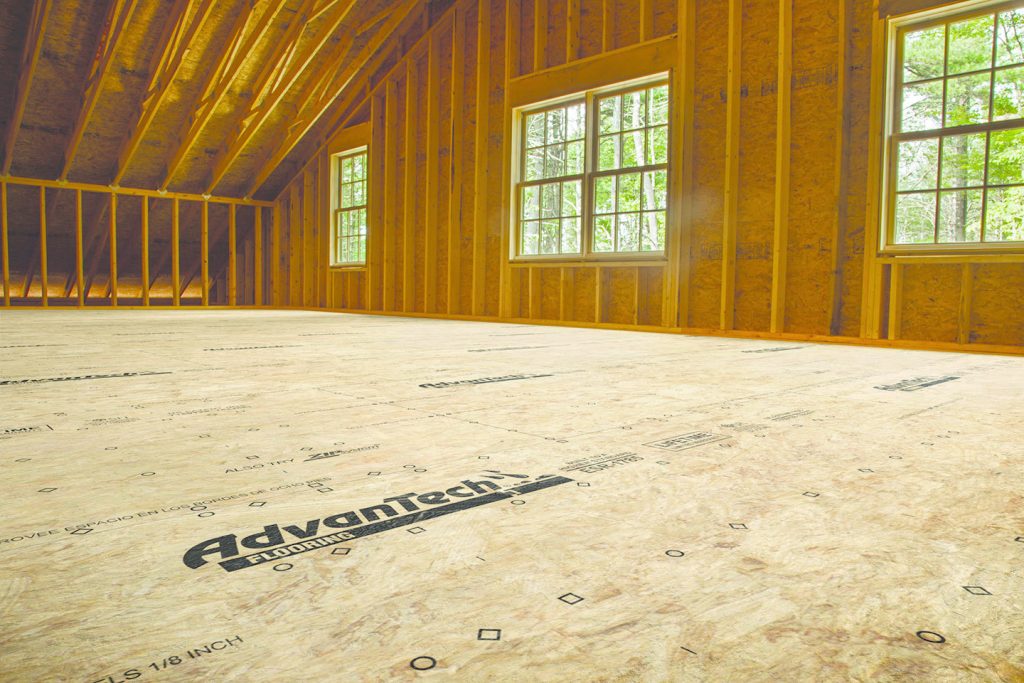

AdvanTech subflooring excels in all three areas.
These include tensile strength, water resistance, and nail-holding power. As a result, you will have consistent backing from edge to edge, keeping things from creaking.
Durability: Advantech flooring panels are considerably more sturdy and long-lasting than standard plywood. It’s more robust, more durable, and more resistant to damage.
Stiffness: The stiffness is substantially greater than that of plywood. It’s far more resistant to bending.
Bending Capacity: Advantech flooring panels are more resistant to deformation than plywood. It requires a greater force to bend it.
Which Plywood Alternative To Choose?
Nothing beats wood regarding a finished product’s beauty, warmth, and texture.
But for those who cannot decide, we hope you can determine which alternatives best suit you.
Firstly, the price you pay should align with the functionality of the product you intend to use. For example, if you’re on a tight budget, you can consider Particle board, RPF, and Ekoply.
Likewise, if you want simplicity, you can choose from GRP, Solid Wood, and Masonite. If you rely on the appearance of only a few colors or patterns, this is what you’re looking for.
Regarding durability, you can go for Polyurethane, HDF, and Baltic Birch Plywood. All of which are stronger, last longer, and are less likely to break.
Ultimately, we cannot say which is better because they all have strong points. As a result, pick the option that serves your purposes the best.
So, we recommend you do your homework. Then plan before choosing the material for your home renovations.
FAQ
Which One Of The Plywood Alternatives Is The Cheapest?

The cheapest plywood alternatives are Particle boards and Ekoply.
These materials are often known as reconstituted wood products. Particleboard and Ekoply are two of the most affordable alternatives to plywood. This is because manufacturers make them from recycled resources.
They’re typically crafted using offcuts of lumber. Residents tag these woods as discarded pieces. The scraps from plywood production are often used to create particle boards.
As a result, homeowners can purchase particle board and Ekoply at a reduced cost.
In most cases, A 4′ x 8′ sheet of particle board used to cost roughly $10 before the COVID outbreak. Nonetheless, the same size sheet might cost as much as $30 or $40 in the market today.
What Is Lighter Than Plywood But Just As Strong?
Polyurethane Model Board is the most lightweight and durable material.
The foam boards are 30%-60% lighter than a comparable sheet of plywood. For example, pine plywood has a density that ranges from 500 to 650 kg/m3. In contrast, Polyurethane weighs 240kg/m3.
With this type of product, you can make stiff material with ease. Its remarkable lightweight and equal durability shine through when reinforced with fiberglass.
As you can see, a polyurethane board is an excellent investment. It can last a service life of 50 years or more. This is because of its waterproof, closed-cell structure.
It also protects it from environmental influences like moisture and airflow.
Overall, these boards are as long-lasting as plywood. In addition, they are watertight and resistant to wear and tear.
Which Of Plywood Alternatives Are Waterproof?
The waterproof plywood alternatives are Polyurethane Board, OSB, RPF, & EKOply. However, Reinforced Polyurethane Boards (RPF) are the most watertight option (RPF).
In contrast to plywood, it has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It only absorbs 1% of its weight in water.
In most cases, great strength is necessary for marine and transportation settings. And RPF mainly achieves this.
Due to its closed-cell structure, reinforced polyurethane foam exhibits very low moisture absorption. As a result, RPF excels in insulating applications. This is where moisture resistance is paramount, such as walls and roofs.
It has a major benefit over conventional insulating options. And it is the only insulating material that can achieve grade 5, even without a concrete layer on the inside face of the brick wall.
Is Birch Plywood the Same As Baltic Birch?
Contrary to popular belief, Birch Plywood is different from Baltic Birch.
Yes, Baltic Birch and birch plywood share a name. However, the two have significant distinctions, like spacing, applications, and costs.
Baltic birch plywood consists of uniformly thin sheets of birch veneer. At the same time, birch plywood has a thin birch veneer on both sides. In addition, it has more delicate layers of pine or poplar in between. Since it’s hollow, it’s less sturdy than Baltic birch plywood.
Spacing: Voids are not an issue with Baltic birch plywood. However, there are gaps or holes within the Birch plywood.
Applications: Baltic birch plywood makes it suitable for furniture and decorative applications. Birch plywood, on the other hand, is mainly used in construction.
Cost: Baltic birch plywood can be expensive. Meanwhile, birch plywood is a low-cost alternative that achieves a similar effect.
Is OSB Better Than Plywood?

No, both are long-lasting materials that showcase toughness and portability.
Here are some of their similarities:
- Both OSB and plywood have the same weather resistance ratings. Similar ratings and standards for efficiency and durability apply to both.
- Upon installation, both materials follow the same set of guidelines for installation.
- Both OSB and plywood have about the same density and weight.
- Both can endure for up to 50 years if homeowners protect them from the elements.
Generally, plywood is a great choice for both flooring and roofing. Yet, it is beneficial for installing a solid floor.
OSB is a fantastic alternative that needs to cover places for moisture exposure. On the other hand, plywood is better suited for jobs that involve a lot of cutting and molding.
Are MDF And HDF Stronger Than Plywood?
HDF is usually seen as better than plywood. This is because it has a higher density, is stronger, and lasts longer. However, compared to MDF, plywood is stronger.
Plywood is second only to solid wood in terms of strength among building materials. However, high-density fibreboard, or HDF, is a more durable alternative to MDF. To compare, MDF is the weakest material among all these but is stronger than particle board.
In most cases, MDF will save you money over plywood. MDF’s smooth surface is ideal for painting. Since MDF is uniform throughout, the finished product will have no gaps or splinters if you decide to cut it. On the other hand, Plywood’s rough surfaces make it unsuitable for intricate carvings.
Meanwhile, HDF is the most robust and naturally water-resistant engineered wood available. As a result, in high-traffic areas like offices, hotels, and theaters, HDF is the material of choice.










Might consider leaving out alternative that are not available in the US such as EKO Plyboard that seems to be only available in the UK.
I was wanting to use this myself but seems no company in the US sells it.